DEEP BLUE PROCESS
For cocktails of innovative enzymes

Benefits
- More efficient enzymes
- High stability
- Wide range of applications
- Low-cost production
Key words
- Innovative enzymes
- Extremozymes
- Nutrition Health
Intellectual Property
- 3 patents
- 1 patent
Laboratory
- IBS
Institutions
- CEA
- CNRS
- UGA
Linksium Continuum
- Maturation
- Incubation
- Commercialization
Results
- Available licenses
Context
Peptides are fragments of proteins that play key roles in our diet, from the taste of our food to its biological properties. Today’s existing solutions for modifying peptides are not effective enough; Deep Blue Process is developing new enzymatic solutions to optimise these processes. The start-up’s objective is to provide manufacturers with new tools to improve our future diet.
Technology
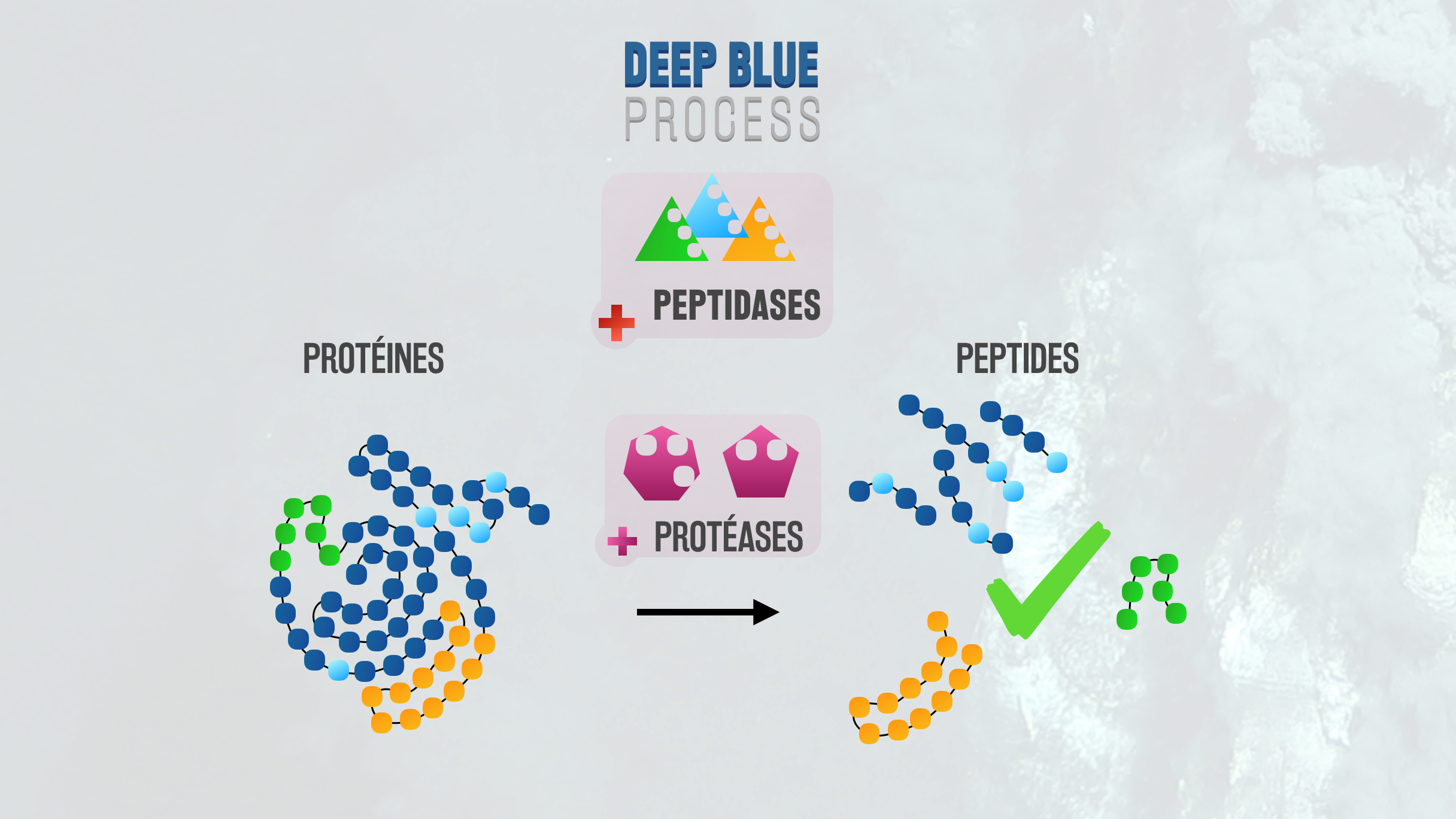
The Deep Blue Process enzymes come from deep-sea organisms that develop in extreme physico-chemical conditions. These enzymes are therefore blessed with exceptional properties of stability and efficiency. The enzyme families used by Deep Blue Process also have very specific targets. These properties, associated with the team’s know-how, enabled the development of an innovative process to finely modify the peptides. This process consists, in particular, of the use of different original combinations of enzymes, which can be immobilised using an innovative method, enabling the “tailored” modification of the properties of hydrolysates or raw food products.
Advantages
The technology used makes it possible to target only those residues that have to be modified, unlike the existing processes that suffer from a lack of efficiency and/or specificity in regard to the targets to be processed. It is therefore possible to eliminate only those residues responsible for the bitter taste of a hydrolysate, or to enrich a hydrolysate in a given peptide, for example, without altering all peptides however. The mixtures of Deep Blue Process enzymes are thus in a position to significantly improve the existing enzymatic processes, or even replace them.
State of progress
Demonstrators have been completed at laboratory level on substrates of agrifood interest such as gluten or a lactoserum protein hydrolysate. We are now capable of piloting this activity and leading it onto certain substrates by playing on the composition of the enzymes used. The team is now focused on optimising the innovative immobilisation process and on demonstrating the activity of the enzymes on industrial production chains.
Applications
- Organoleptic modifications of protein hydrolysate
- Biotechnology for human nutrition
- Production of bioactive peptides
- Infant nutrition
- Diet of the elderly or people with digestive system disorders
- Diet of pets

