WATTPILL
Using the energy of the organism

Benefits
- Energy produced from the fuels present in the organism
- Creation of natural power for medical devices
Key words
- Biobattery
- Glucose
- Implantable
- Human health
Intellectual Property
- 2 patents
Laboratory
- TIMC-IMAG
Institutions
- CNRS
- GRENOBLE INP-UGA
- UGA
Linksium Continuum
- Maturation
- Incubation
- Acceleration
Results
- Incorporated startups
Context
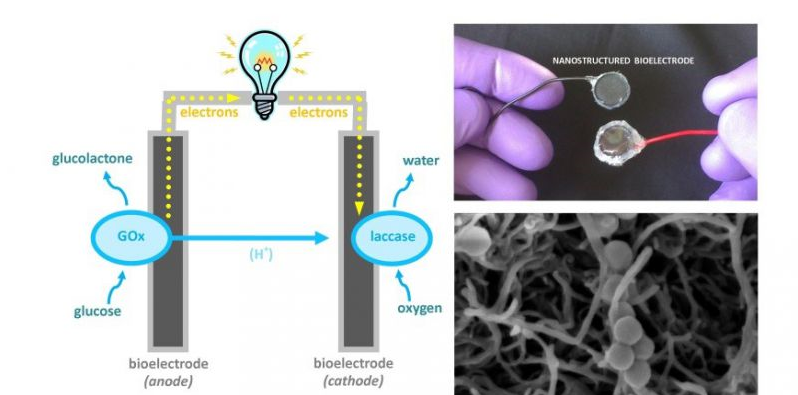
This concerns the design of an implantable enzyme-based glucose biobattery, original in its manufacturing method and its biocompatibility.
Technology
This biobattery is composed of electrodes containing enzymes, conductors, electrochemical mediators, if necessary, and a “binder”. The most effective binder is a natural and biocompatible polymer, modified to be non-degradable for use in the physico-chemical conditions of the extra-cellular liquid of mammals.
All of these elements are compressed into two semi-permeable and non-biodegradable “pastilles”, with controlled porosity to allow the entry of the fuels (glucose and oxygen), while guaranteeing that the device is thoroughly sealed. The entire device can be sterilised. During the implantations, the voltage and intensity produced are measured and monitored by wireless communication.
Advantages
It has been demonstrated that a battery composed of enzymes contained in a bag made from semi-permeable membranes can be implanted in an animal. This biobattery not only has one of the best performance levels (approximately 0.5 µW/µL electrodes), but is also the first (and at present the only one) to have been implanted into mammals, producing more power than that required by a pacemaker (40 µW).
State of progress
The battery is currently the only enzyme-based biobattery to have demonstrated its ability to remain operational for several months inside a mammal.
Applications
In the short term, on the animal health market, where biochips have a promising future.
In the medium term, by capitalising on veterinary data, this biobattery can be used to power any implantable medical device.

