SAXOL
Incorporated startups
A new therapeutic agent with dual properties: it synergises taxanes and protects against chemo-induced neuropathy

Linksium Contact
Laurène El Bahhaj
+33 (0)7 76 23 29 19 laurene.elbahhaj@linksium.fr
SAXOL
Philippe Bordeau, CEO
+33 (0)6 08 52 26 31
Benefits
- Reduction of taxane doses without loss of therapeutic efficacy
- Reduced toxicity
- Prevention of chemo-induced peripheral neuropathy
Key words
- Taxane chemotherapy
- Peripheral neuropathies
- Cancer
Intellectual Property
- 1 patent
Partnerships & Rewards
- 2025 French Deeptech Innovation Competition Winner
Laboratory
- IAB
Institutions
- CNRS
- INSERM
- UGA
Linksium Continuum
- Maturation
- Incubation
Results
- Incorporated startups
Context
Taxane-based chemotherapies are among the most frequently used cancer therapies. However, they have adverse effects such as neuropathy (CIPN), which have a major impact on patients' quality of life. These neuropathies are often the cause of treatment discontinuation and compromise the success of the cancer treatment. In 1 out of 4 cases, they may even persist irremediably.
Technology
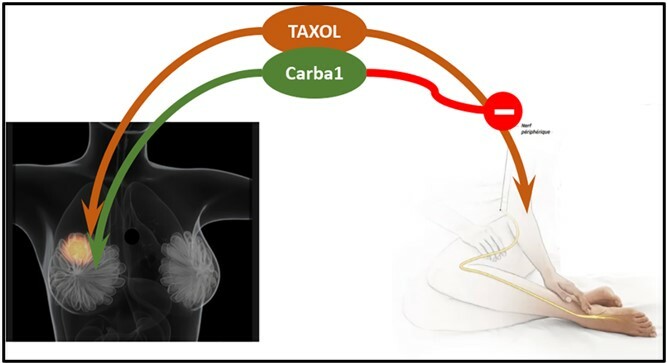
SAXOL project is based on the discovery of Carba1, which acts in synergy with Taxol®, allowing doses to be reduced while maintaining its therapeutic effectiveness. It also activates a metabolic enzyme, which has a neuroprotective effect.
Advantages
- Reduction of taxane doses for a preserved therapeutic effect: limitation of toxicities due to taxane formulations, reduction of resistance.
- Neuroprotective effect preventing the onset of neuropathies for which there is no effective preventive treatment.
State of progress
- Validated and patented method for the synthesis of Carba1
- Synergistic effect of the Carba1/Taxol combination validated in vivo in a mouse tumour model
- ADME-Tox: performed, no warning signals
- Neuroprotection: demonstrated on neurons in vitro. Target and mechanism of action known.
Applications
- Cancer chemotherapy
- Prevention of chemo-induced peripheral neuropathy
- Potential prevention of other neuropathies (diabetes) and neurodegenerative diseases

Close projects index
